What is Defect/Bug Life Cycle in Defect Tracking?
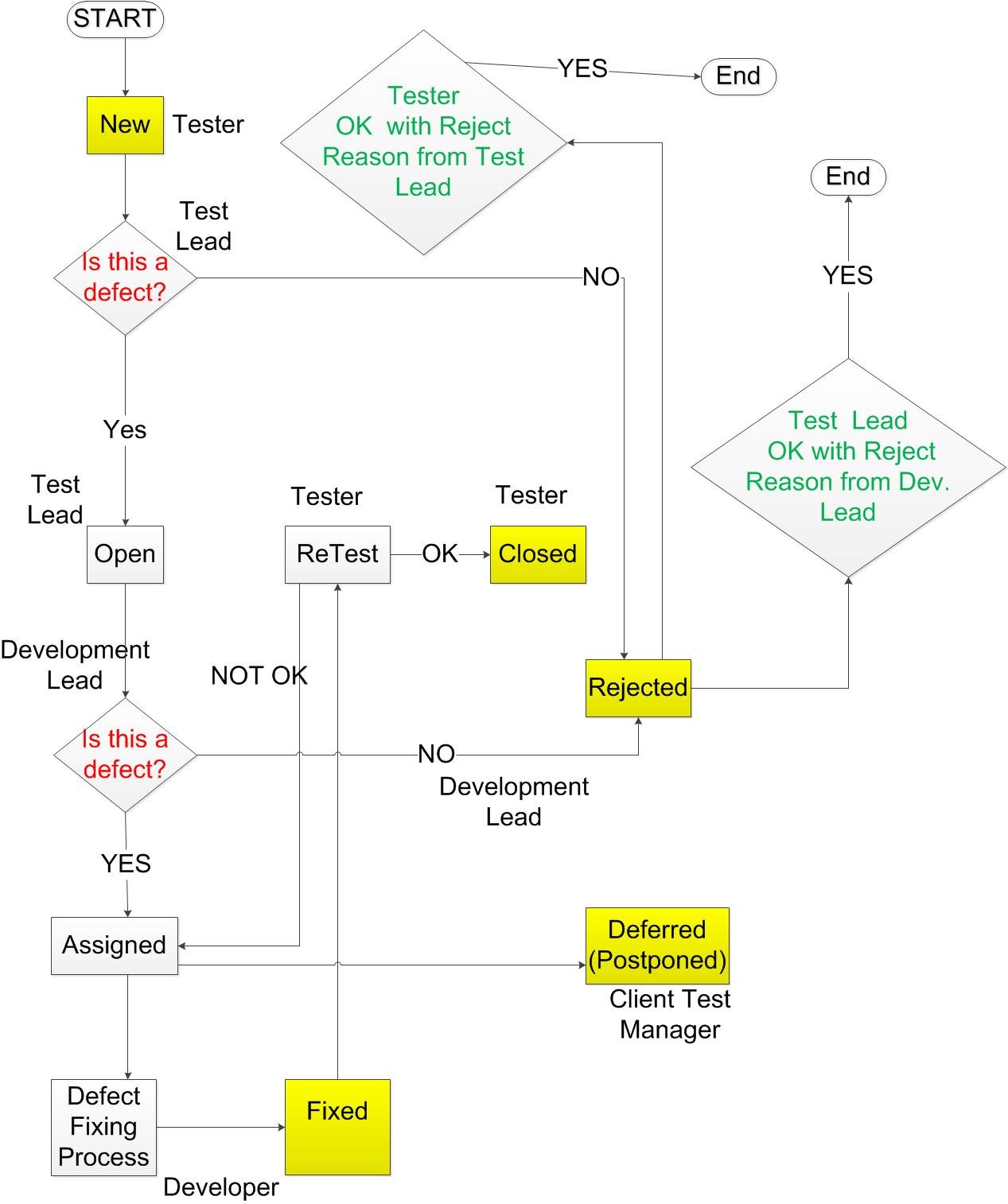
A defect in a Software testing process will undergo different status like New, Open, Assigned, Rejected, Fixed, Reopen, ReTest, Closed, Deferred etc. before being considered as Closed or Rejected or Deferred.
So there are 3 different situations possible here in any manual or automated testing in Defect Management.
- New – Closed
- New – Rejected
- New – Deferred (Postponed)
The time taken for the defect to be closed or rejected or deferred is called as a BUG LIFE CYCLE.
Explanation for Status:
| Status | Description | Set By |
|---|---|---|
|
New |
A new defect detected by a tester |
Test Team |
|
Open |
A defect that has been reviewed and verified as a true defect |
Test Lead |
|
Rejected |
A defect that has been found not to be a defect |
Development Lead |
|
Assigned |
A defect that has been verified by development and is now assigned to developers for fixing |
Development Lead |
|
Fixed |
A defect that has been fixed and is ready for retesting |
Developer |
|
ReTest |
A defect that has been fixed by developers, which is once again tested to be closed. |
Test Team |
|
Reopen |
A defect that has failed testing during ReTest |
Test Team |
|
Closed |
A defect that has successfully passed retesting |
Test Team |
|
Deferred |
A defect that has been mutually agreed to move to the next release among Business, Test Lead and Development Lead. |
Client Test Manager |
Defect Tracking:
With the email application example, we will explain the Defect/bug life cycle about how a new defect is created and tracked.
Once the email application development is completed, the tester tests the login page. While testing the login page, the tester founds out that the username field allows duplicate names. So the tester logs in to Test Management Software and registers a new defect.
Role of a Test Lead, Tester, Development Lead and Developer (DBA) in closing the defect:
| Tester | Finds Defect and reports to the Testing Lead. |
| Test Lead | Verifies defect. Since this defect is a valid defect, creates a NEW status to the defect and this defect is passed to the Development Team. |
| Development Lead | Verifies defect: Since this defect is a valid defect, bug is assigned the status ASSIGNED and assigned to the developer (DBA). |
| Developer | Developer works on this issue and creates PRIMARY KEY on that table and changes the status to FIXED and this is reported to TESTING LEAD. |
| Testing Lead | Changes the status to RETEST and assigns it to the tester |
| Tester | The tester retests and if everything is OKAY, status will be changed to CLOSED |
Other situations that arise during the handling of defects:
- Tester reports to Testing Lead about a defect and Test Lead rejects it.
- Test Lead is okay with the defect created by tester and reports the defect to the Development Lead and Development Lead rejects it.
- Test Lead, Developer Lead is okay with defect and Developer works on the defect and reports to Testing Lead that the defect has been resolved. Again, Tester retests and reports that the defect has not been resolved and not closed. So, he reopens the defects once again.
- Based on the priority or severity (The severity of the defect may be low, medium, high, critical and cosmetic etc. ) of the defect, the defect may not be closed at all or it may be deferred (postponed).
Defect/Bug Life Cycle Flow Chart: